
Published on Angewandte Chemie (5 July 2021)
Author(s): Dr. Ning Cai, Fengzhu Li,, Yatong Chen, Ruixi Luo, Tonghui Hu, Francis Lin, Dr. Shek-Man Yiu, Danjun Liu, Dr. Dangyuan Lei, Dr. Zonglong Zhu, Prof. Alex K.-Y. Jen
Abstract
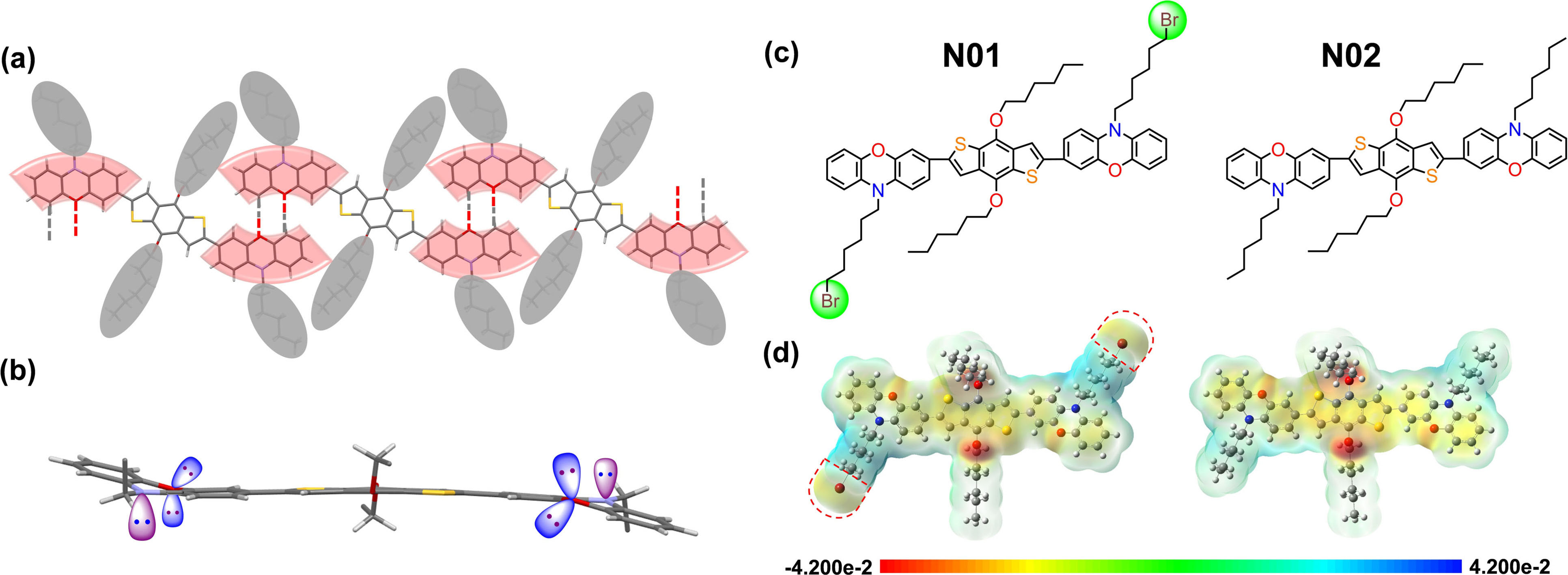
Delicately designed dopant-free hole-transporting materials (HTMs) with ordered structure have become one of the major strategies to achieve high-performance perovskite solar cells (PSCs). In this work, we report two donor-π linker-donor (D-π-D) HTMs, N01 and N02, which consist of facilely synthesized 4,8-di(n-hexyloxy)-benzo[1,2-b:4,5-b′]dithiophene as a π linker, with 10-bromohexyl-10H-phenoxazine and 10-hexyl-10H-phenoxazine as donors, respectively. The N01 molecules form a two-dimensional conjugated network governed by C−H⋅⋅⋅O and C−H⋅⋅⋅Br interaction between phenoxazine donors, and synchronously construct a three-dimension lamellar structure with the aid of interlaminar π–π interaction. Consequently, N01 as a dopant-free small-molecule HTM exhibits a higher intrinsic hole mobility and more favorable interfacial properties for hole transport, hole extraction and perovskite growth, enabling an inverted PSC to achieve a very impressive power conversion efficiency of 21.85 %.
Read more: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/anie.202107020