Opportunity
The next generation of wireless technology has arrived. With the emergence of fifth generation (5G) broadband cellular networks, the global demand for high-quality connectivity is expected to increase exponentially in the foreseeable future. Researchers have turned to the millimeter (MM) wave radio frequency spectrum, a largely untapped source of raw data bandwidth, to develop new 5G wireless technologies. Riding this wave, the current invention describes a novel complementary antenna for transmitting and receiving radio frequency signals that could help high-technology companies harness the power of MM communications for 5G, radar, and auto-driving applications. Compared with existing antennas operating in MM wave frequencies, the proposed device provides a much wider operating bandwidth, making it an exceptional candidate for communications and data transmission development in the era of 5G.
Technology
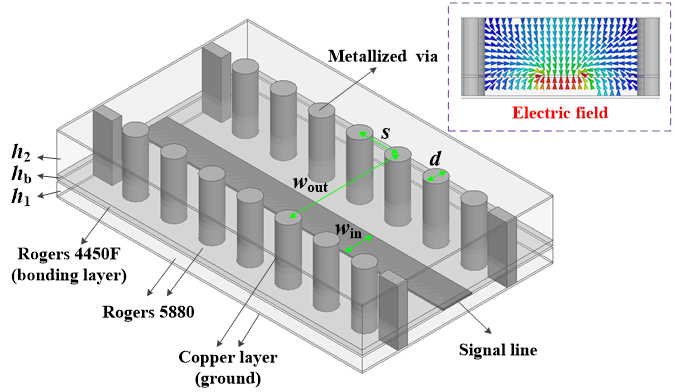
The novel antenna is built from stacked laminates with metallic planar patterns, whose layers are connected by metallic pins. It has a complementary structure, comprising a pair of orthogonally oriented sources: a magnetic dipole and an electrical dipole. The magnetic dipole source involves two parallel planar plates, while the electrical dipole source is provided by two pairs of metallic pins. The two sources are excited simultaneously by a probe. This probe is linked to a feed line—connecting the antenna with a radio transmitter or receiver—that offers the advantage of wideband unimodal operation, enabling the antenna to operate over a wide frequency band. Furthermore, the complementary nature of the two sources (magnetic and electrical) allows the antenna to produce unidirectional radiation.
Advantages
- Comparable existing antennas typically exhibit bandwidths up to 20%. The proposed complementary antenna has a much wider operating bandwidth, making it desirable for MM wave applications in the 5G era.
- Smaller gain variation than previously reported end-fire complementary antennas.
- Design of feed line improves on previous feed lines by reducing size and improving interconnectivity, further enhancing realizable bandwidth.
- Superior electromagnetic characteristics compared with existing antennas, including large impedance bandwidth, symmetric patterns, low cross-polarization and low back radiation.
- Unlike some existing antennas, the proposed antenna is suited to various terminal devices, especially thin and portable devices.
Applications
- Compact antenna can be used in phased array designs for wide-angle beam scanning, which is conducive to communications and radar applications.
- Enhancement of MM wave communication for auto-driving technologies.
- Enhancement of MM wave communication for radar applications.
- Enhancement of MM wave communication for development of 5G technologies.