Involved Members: Prof. Kenneth Mei Yee LEUNG
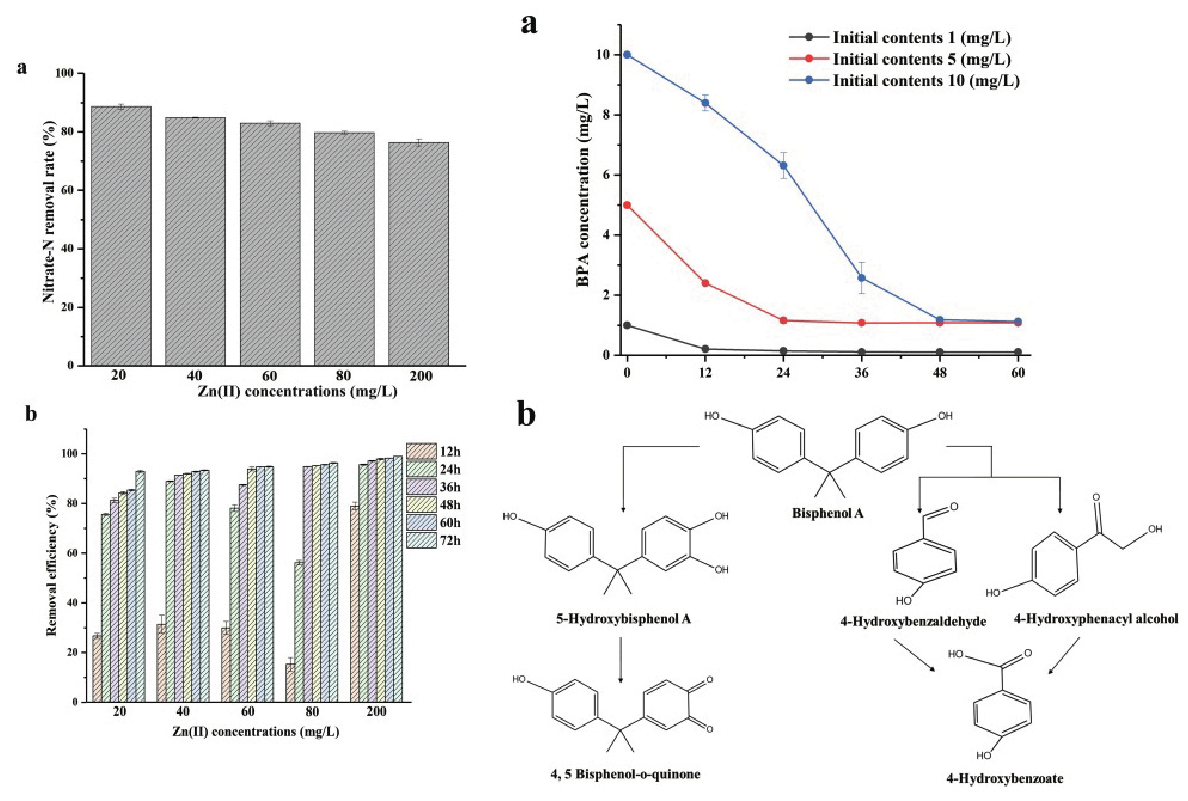
High concentrations of heavy metals and other pollutants affect microbial activity in the wastewater treatment system and impede biological denitrification process. A novel Zn(II)-resistant aerobic denitrifier (Pseudomonas stutzeri KY-37) was isolated with potential in biodegradation and removal of Bisphenol A (BPA). Its capability in concurrent removal of nitrogen, zinc, and BPA was tested. Nitrogen removal efficiency achieved 98.5% in 12h. Zn(II) removal efficiency reached more than 95%, while the maximum BPA removal efficiency reached 88.8%. Mechanisms of BPA removal included microbial degradation and adsorption on extracellular polymeric substances.
Reference:
Hong, P., Zhang, K., Dai, Y., Yuen, C.N., Gao, Y., Gu, Y., Leung, K.M.Y. (2022). Application of Aerobic Denitrifier for Simultaneous Removal of Nitrogen, Zinc, and Bisphenol A from Wastewater. Bioresource Technology, 354, 127192. (impact factor 11.889)