Opportunity
Prostate zonal segmentation is an important component of prostate cancer diagnosis, treatment planning, and disease prognosis. This assessment is often manually performed by clinicians, resulting in a drain on clinicians’ time and causing human factors to influence the accuracy of the assessment. Cutting-edge approaches to prostate zonal segmentation employ deep learning based on 3D convolutional neural networks (CNN). These 3D CNNs exhibit strong performance when massive levels of training data are available – and when the training data share the same distribution with test data. However, these conditions may not necessarily apply to real-world scenarios, since it is not feasible to collect this level of data for each medical center and imaging device.
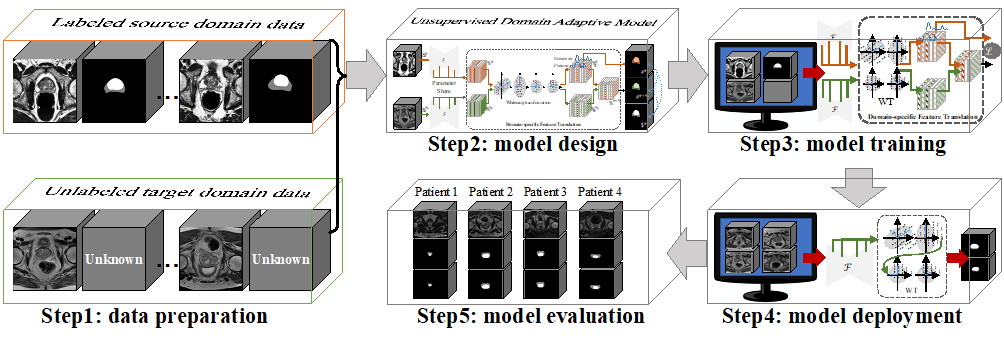
This invention employs labeled open-source prostate zonal segmentation data to augment a 3D CNN’s knowledge of target data. To reduce the domain gap between the different data sets, this invention also dynamically translates labeled source data to target data using a domain-specific feature translation method. This helps prevent performance degradation.
Technology
Source domain data for the 3D CNN is provided from three annotated open-source datasets. It is then randomly divided into three subsets: a training set, a validation set, and a test set. For this invention, the validation and test sets were labelled by two experienced radiologists. The 3D CNN is pre-trained with the labelled source data. Then this labelled source domain data, along with the unlabelled target domain data, are simultaneously fed into a model that adapts the data to the target domain. Since there will be a gap between the source data and the target domain, this invention uses domain-specific feature translation to dynamically and gradually translate the labelled source data. The model’s performance in prostate zonal segmentation is then evaluated in accordance with standard validation metrics.
Advantages
- This invention can reduce the time and costs required for prostate cancer diagnosis, treatment planning and disease prognosis.
- This invention can liberate clinicians from the tedious work of annotating prostate zonal segmentation using current methods.
- Unlike current state-of-the-art 3D models for prostate zonal segmentation, this invention does not require massive levels of annotated training data for each medical center or imaging device.
- This invention can reduce the domain gap and facilitate the adaptation of the model on target data, thereby improving performance.
Applications
- Cancer hospitals and centers
- Diagnostic laboratories